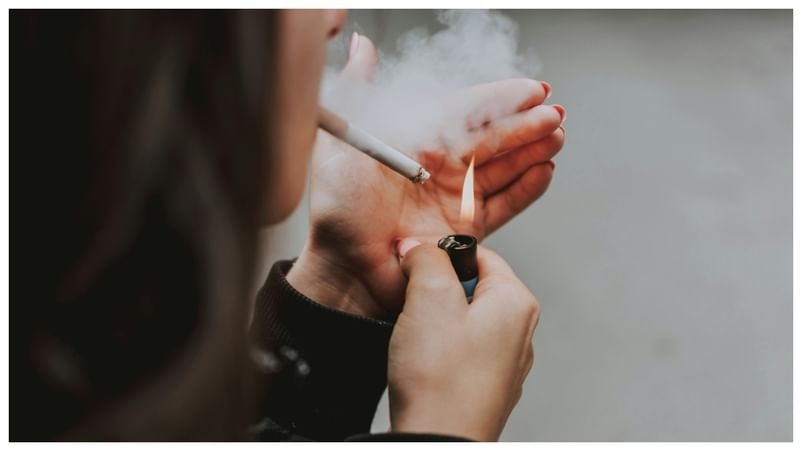
Quitting smoking is widely known to improve physical health, but what many people don’t realize is that it also brings significant benefits to mental health. While smoking may seem to temporarily relieve stress and anxiety, in reality, it worsens overall mental well-being in the long run.
Dr. Sayantani Mukharjee, Psychiatrist at Sahyadri Super Speciality Hospital, Hadapsar, Pune, explains that nicotine tricks the brain into believing it’s reducing stress. However, it actually creates a cycle of dependence, withdrawal, and increased anxiety, leading to long-term mental health struggles.
When individuals quit smoking, they experience:
Reduced anxiety and depression
Improved mood and emotional stability
Better cognitive function
Stronger mental resilience
Enhanced social interactions and self-esteem
Understanding these benefits can motivate individuals to quit smoking and embrace a healthier, happier life.
The Psychological Trap of Smoking: Why It Feels Like Stress Relief
Many smokers believe smoking helps them relax, but this is an illusion. Nicotine withdrawal creates stress, irritability, and anxiety—feelings that are briefly relieved by another cigarette. This leads to a harmful cycle:
- Nicotine creates a temporary “high” by stimulating dopamine release (the brain’s pleasure chemical).
- As nicotine levels drop, withdrawal symptoms set in, causing stress and restlessness.
- Smoking another cigarette brings temporary relief, reinforcing the habit.
The result? Smokers become dependent on nicotine to feel “normal,” even though their overall stress levels increase over time.
Once a person quits smoking, this cycle breaks, and their natural stress response improves, leading to lasting mental clarity and emotional stability.
How Quitting Smoking Improves Mental Health
1. Mood Stabilization & Reduced Anxiety
Dr. Mukharjee highlights that quitting smoking can improve mood as effectively as taking antidepressants. Smokers often experience:
- Lower levels of anxiety and depression after quitting.
- Less aggression and mood swings, which are common during nicotine withdrawal cycles.
- A greater sense of calm and emotional balance in daily life.
2. Enhanced Cognitive Function
Quitting smoking boosts brain performance, leading to:
- Improved concentration and focus
- Better memory and faster information processing
- Increased mental resilience, making it easier to handle stress
Studies show that smokers tend to experience cognitive decline earlier in life, while quitting protects brain function and reduces the risk of dementia and memory loss.
3. Social & Psychological Benefits
- Freedom from social stigma: Many smokers feel self-conscious due to negative perceptions associated with smoking. Quitting improves self-esteem and social confidence.
- Stronger relationships: Smokers often face restrictions in public places, at work, or even in relationships. Quitting smoking removes these barriers, leading to better personal and professional interactions.
4. Better Response to Mental Health Treatment
Smoking affects the metabolism of psychiatric medications, including antidepressants and antipsychotics. When a person quits smoking:
Their medications work more effectively.
They require lower doses for the same therapeutic effect.
They experience better long-term mental health stability.
Long-Term Mental Health Benefits of Quitting Smoking
Within a Few Days: Reduced stress, clearer thinking, and improved sleep.
After a Few Weeks: Improved mood, fewer mood swings, and enhanced emotional stability.
Long-Term: Lower risk of depression, better cognitive function, and greater overall happiness.
Quitting smoking is one of the best decisions for both physical and mental health. By breaking free from nicotine addiction, individuals gain emotional stability, mental clarity, and a better quality of life.
The journey to quitting may be challenging, but the mental health rewards are truly life-changing!

 Desk
Desk Share
Share